That is, each entry made on the debit side has a corresponding entry (or coverage) on the credit side. With the accounting equation expanded, financial analysts and accountants can better understand how a company structures its equity. Additionally, analysts can see how revenue and expenses change over time, and the effect of those changes on a business’s assets and liabilities. The accounting equation shows how a company’s assets, liabilities, and equity are related and how a change in one results in a change to another. In the basic accounting equation, assets are equal to liabilities plus equity. This straightforward relationship between assets, liabilities, and equity is the foundation of the double-entry accounting system.
What is the approximate value of your cash savings and other investments?
Accounts receivable list the amounts of money owed to the company by its customers for the sale of its products. Assets include cash and cash equivalents or liquid assets, which may include Treasury bills and certificates of deposit (CDs). However, this scenario is extremely rare because every transaction always has a corresponding entry on each side of the equation. Analyze a company’s financial records as an analyst on a technology team in this free job simulation. Metro Corporation earned a total of $10,000 in service revenue from clients who will pay in 30 days.
Components of the Basic Accounting Equation
The purpose of this article is to consider the fundamentals of the accounting equation and to demonstrate how it works when applied to various transactions. One of the main financial statements (along with the balance sheet, the statement of cash flows, and the statement of stockholders’ equity). The income statement is also referred to as the profit and loss statement, P&L, statement of income, and the statement of operations.
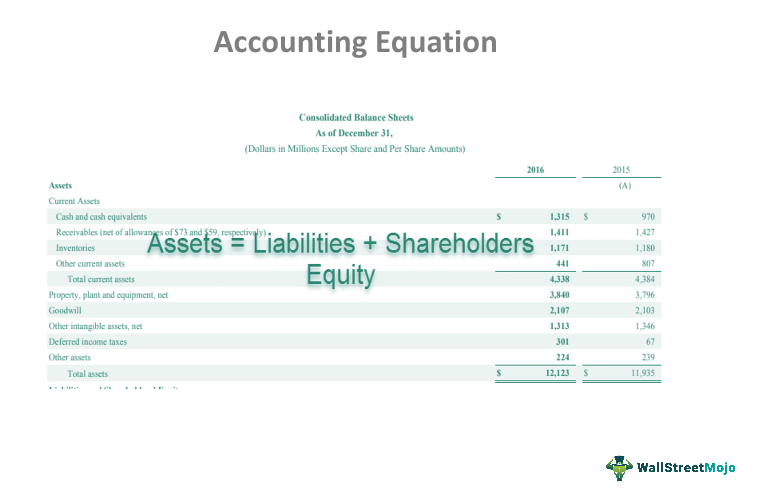
The accounting equation And how it stays in balance
- This then allows them to predict future profit trends and adjust business practices accordingly.
- The double-entry practice ensures that the accounting equation always remains balanced, meaning that the left-side value of the equation will always match the right-side value.
- Equity represents the portion of company assets that shareholders or partners own.
- On 12 January, Sam Enterprises pays $10,000 cash to its accounts payable.
The accounting equation focuses on your balance sheet, which is a historical summary of your company, what you own, and what you owe. This transaction would reduce cash by $9,500 and accounts payable by $10,000. The difference debt to total assets ratio financial accounting of $500 in the cash discount would be added to the owner’s equity. On 12 January, Sam Enterprises pays $10,000 cash to its accounts payable. This transaction would reduce an asset (cash) and a liability (accounts payable).
What Happens if the Accounting Equation Is Not Balanced?
In this case, Speakers, Inc. uses its cash to buy another asset, so the asset account is decreased from the disbursement of cash and increased by the addition of installation equipment. Let’s take a look at the formation of a company to illustrate how the accounting equation works in a business situation. When a company purchases goods or services from other companies on credit, a payable is recorded to show that the company promises to pay the other companies for their assets. If a transaction is completely omitted from the accounting books, it will not unbalance the accounting equation. The accounting equation is fundamental to the double-entry bookkeeping practice. Its applications in accountancy and economics are thus diverse.

At this point, let’s consider another example and see how various transactions affect the amounts of the elements in the accounting equation. If the net amount is a negative amount, it is referred to as a net loss. The assets have been decreased by $696 but liabilities have decreased by $969 which must have caused the accounting equation to go out of balance. To calculate the accounting equation, we first need to work out the amounts of each asset, liability, and equity in Laura’s business.
Our PRO users get lifetime access to our accounting equation visual tutorial, cheat sheet, flashcards, quick test, and more. This is how the accounting equation of Laura’s business looks like after incorporating the effects of all transactions at the end of month 1. In this example, we will see how this accounting equation will transform once we consider the effects of transactions from the first month of Laura’s business. If you’re still unsure why the accounting equation just has to balance, the following example shows how the accounting equation remains in balance even after the effects of several transactions are accounted for. The accounting equation shows the amount of resources available to a business on the left side (Assets) and those who have a claim on those resources on the right side (Liabilities + Equity).
Accountants and members of a company’s financial team are the primary users of the accounting equation. Understanding how to use the formula is a crucial skill for accountants because it’s a quick way to check the accuracy of transaction records . Due within the year, current liabilities on a balance sheet include accounts payable, wages or payroll payable and taxes payable. Long-term liabilities are usually owed to lending institutions and include notes payable and possibly unearned revenue. Before technological advances came along for these growing businesses, bookkeepers were forced to manually manage their accounting (when single-entry accounting was the norm). Of course, this lead to the chance of human error, which is detrimental to a company’s health, balance sheets, and investor ability.